How to Properly Calculate EBITDA for Improved Financial Analysis in 2025
Understanding how to calculate EBITDA is essential for anyone involved in financial analysis, business valuation, or investment evaluation. EBITDA, which stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization, provides a clearer picture of a company’s operational profitability by focusing on its earnings without the impacts of financing and accounting decisions. In this article, we will explore the EBITDA calculation, understand its formula, and how it can enhance your financial performance analysis in 2025.
What is EBITDA? Understanding the Definition
The term EBITDA is often used in financial circles to measure a company’s overall financial performance. It reflects a company’s earnings derived from its core business operations, providing insights into its operating income without the effects of capital structure, tax rates, and non-cash accounting items like depreciation and amortization. Essentially, EBITDA is seen as a better indicator of business profitability than net income because it strips away all the expenses that don’t result from the core business functions.
The Importance of EBITDA in Business Valuation
Using EBITDA as a measure gives investors a standardized way to compare profitability across similar companies in the industry. Analyzing EBITDA margins can provide insights into how efficiently a company converts revenue into earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. This metric is particularly beneficial in industries with varying capital structures or different tax environments since EBITDA focuses on operational performance.
Differences Between EBITDA and Other Financial Metrics
While many financial metrics can provide valuable insights, each serves a different purpose. For instance, an income statement gives a comprehensive overview of a company’s revenue and expenses over a period, but it may not reveal the true operating performance due to high financing costs or one-time tax burdens. Similarly, using net income can be misleading because it includes non-operating income and expenses. EBITDA, in contrast, provides a cleaner perspective on cash flow generated from core operations.
The EBITDA Calculation: Formula and Steps
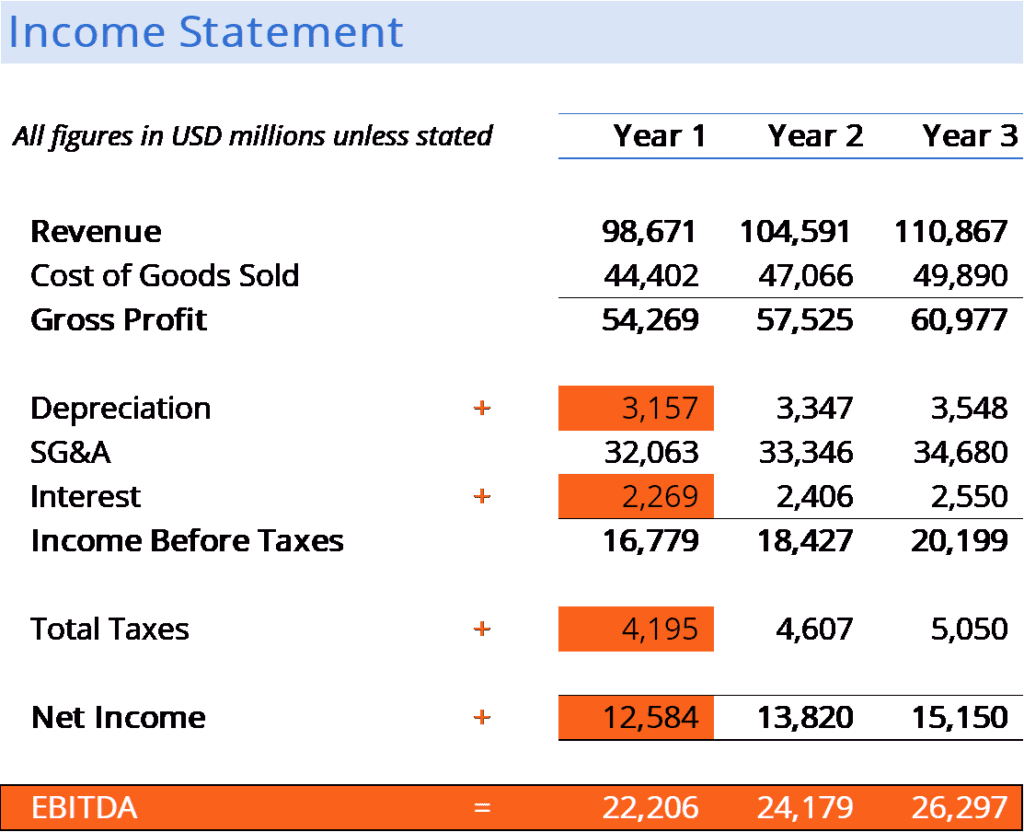
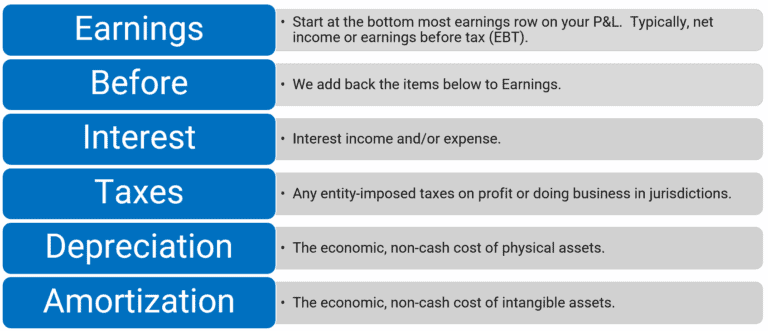
To accurately calculate EBITDA, you need to start with the company’s net income, then add back the interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization expenses. The formula is represented as follows:
EBITDA = Net Income + Interest + Taxes + Depreciation + Amortization
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating EBITDA
- Start with Net Income</ if available from the profit loss statement.
- Add back any interest expenses since they depend on financing decisions, not operational profitability.
- Include taxes, as these can vary greatly depending on the jurisdiction, influencing the final earnings.
- Then, add back Depreciation and Amortization because these are non-cash expenses that do not affect operational cash flow.
This method allows you to derive a clearer picture of operating efficiency, allowing for better financial performance assessments and strategic planning.
Adjusted EBITDA: Enhancing the Standard Metric
In many cases, analysts recommend an Adjusted EBITDA that removes non-recurring items and expenses not inherent in the business’s normal operations. This version is particularly useful for financial forecasts, cash flow management, and investment evaluation. By making these adjustments, stakeholders can accurately assess the ongoing profitability and health of a business without the noise caused by extraordinary items.
Applications and Benefits of EBITDA in Financial Analysis
EBITDA is a powerful tool in the financial analyst’s toolkit; it has several broader applications, especially in evaluating performance, cash flow, and market valuation.
Utilizing EBITDA for Business Valuation and Comparison
EBITDA plays a crucial role in determining a company’s value during mergers and acquisitions or other valuation exercises. By analyzing EBITDA, potential acquirers can ascertain a suitable purchase price based on comparable companies’ valuation multiples. This form of comparative analysis is essential in making informed investment decisions.
EBITDA and Cash Flow Analysis
Many believe that EBITDA approximates cash flow, drawing attention to its cash-generating potential. A strong EBITDA indicates high operational cash flow health, which is vital for fulfilling debt levels, capital budgeting, and sustaining growth. Thus, emphasizing EBITDA in your financial statement analysis can enhance overall financial stability assessments.
The Role of EBITDA in Performance Measurement
Tracking EBITDA over time allows businesses to establish profitability trends while also setting benchmarks against industry comparables. Understanding these trends becomes pivotal in strategic planning and drives operational efficiency improvements.
Key Considerations When Using EBITDA
While EBITDA is insightful, it’s essential to consider its limitations, especially in comprehensive financial analysis.
Limitations of EBITDA as a Financial Metric
One of the core limitations of EBITDA is that it ignores critical expenses related to debt and reinvestment needs. Businesses with high levels of debt might show strong EBITDA yet face severe cash flow problems, misleading investors regarding financial sustainability. Moreover, the omission of depreciation may overlook necessary capital expenditures required to maintain operational stability.
Total Financial Analysis: Beyond EBITDA
Considering EBITDA in your financial metrics toolkit is vital, but it should always be used in conjunction with other measures such as net income, cash flow from operations, or free cash flow to provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial standing. A holistic approach that includes multiple analyses ensures that any stakeholders have a complete landscape of operational health.
Future Trends in EBITDA Utilization for Financial Analysis
As businesses continue to evolve, it’s anticipated that the methods and applications of EBITDA will adapt alongside trends such as raw data processing and advanced financial modeling techniques. Utilizing technology will foster more accurate forecasting and real-time performance evaluation, enhancing how analysts assess business profitability. As the financial landscape evolves, knowledge around EBITDA, alongside other metrics, will play a pivotal role in determining investment strategies.
Key Takeaways
- EBITDA is crucial for understanding a company’s operational efficiency, focusing on earnings before accounting impacts.
- The calculation of EBITDA enables effective comparison across similar businesses, particularly in valuation scenarios.
- Using Adjusted EBITDA can improve the accuracy of operational performance analysis.
- While EBITDA offers depth, it should never be standalone; comprehensive financial analysis requires multiple financial metrics.
- Future trends may enhance the usefulness of EBITDA through advanced analytical techniques and technology integration.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between EBITDA and cash flow?
While EBITDA provides an indicator of operational performance by focusing on earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization, cash flow reflects the liquidity of the company. Cash flow analysis incorporates all cash inflows and outflows, suggesting short-term viability. Operators should not rely solely on either metric but consider both in any financial forecasting.
2. How can EBITDA impact investment strategies?
Investors often use EBITDA as a metric to assess profitability and compare potential investments. A company with strong EBITDA margins may be more attractive due to its improved operational efficiency and profit margins, making investments more calculated. Therefore, incorporating EBITDA can guide investment planning and resource allocation.
3. Can EBITDA be negative? What does this indicate?
Yes, EBITDA can be negative, which may indicate that a company’s operating expenses exceed its earnings. This scenario is concerning for stakeholders as it suggests underlying profitability issues, necessitating a deeper check into other key financial metrics for appropriate risk assessment.
4. How frequently should companies evaluate their EBITDA?
Setting a consistent schedule, such as quarterly or annually, for evaluating EBITDA is advisable. This frequency allows for a better understanding of disparities in financial performance over time and encourages adjustments to business strategies based on comparative analysis.
5. How is EBITDA relevant in conducting financial ‘what-if’ analyses?
EBITDA can serve as the backbone of financial modeling, providing a foundation for exploring various scenarios and adjustments. It empowers stakeholders to assess how different cost structures or external conditions might influence operational performance and, subsequently, profitability.
6. What role does EBITDA play in assessing company value?
EBITDA acts as a key measure for many valuation multiples and assessment frameworks, enabling investors to gauge whether a firm is priced effectively based on its operational performance compared to peers in the industry. Utilizing EBITDA in this context enhances the ability to make informed investment decisions.
7. Why should businesses strive to improve their EBITDA margins?
Improving EBITDA margins reflects enhanced operational efficiency and reduced costs, which ultimately leads to improved cash flow and overall profitability. Companies with rising EBITDA margins are positioned for growth and can attract more investors, leading to better market valuation.