“`html
Effective Ways to Calculate Percent Yield: A Simple Guide for 2025
Understanding how to effectively calculate percent yield is essential for anyone working in chemistry or related fields. The concept of percent yield plays a vital role in evaluating the efficiency of chemical reactions and maximizing output. In this guide, we will explore the percent yield formula, the significance of both actual and theoretical yield, and practical strategies to improve yield in various chemical processes. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Percent Yield in Chemistry
Percent yield is a crucial metric in chemical experiments that helps scientists evaluate the success of a reaction. It compares the actual yield obtained from a chemical reaction to the theoretical yield, which is the maximum possible amount of product that could be formed according to stoichiometric calculations. To determine percent yield, the percent yield formula is straightforward:
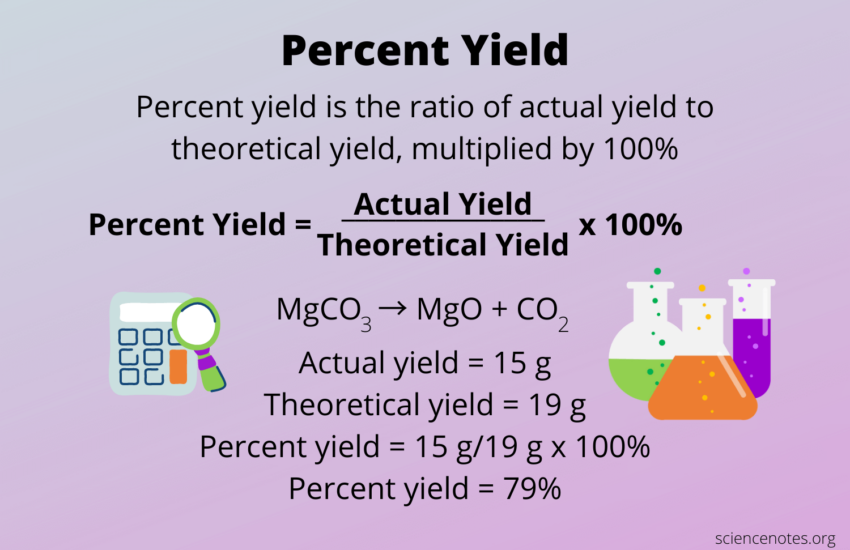
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100%. This metric is not just a number; it reflects the efficiency of the chemical reaction yield and can reveal important data about the reaction’s performance.
Percent Yield Formula Explanation
Understanding the constituent parts of the percent yield formula is essential for correct implementation. The theoretical yield is calculated based on the initial amounts of reactants. It assumes complete conversion without any losses. Conversely, the actual yield is the mass of product actually collected post-reaction. Knowing how to compute these values is critical for interpreting percent yield meaning. For example, if a reaction yields 30 grams of product when theoretically it should yield 50 grams, the percent yield would be (30g/50g) x 100% = 60%. This indicates that while the reaction was partially successful, there’s room for improvement.
The Significance of Percent Yield in Reactions
Understanding percent yield is vital for evaluating the efficiency of chemical reactions. A high percent yield indicates that most reactants were successfully converted into products, facilitating process sustainability and economic viability. On the other hand, a low percent yield could highlight inefficiencies during the reaction, providing insight into potential improvements. Factors affecting percent yield include reaction conditions, purity of reactants, and measurement accuracy. This understanding allows chemists to optimize reactions and improve overall yield performance, thereby saving time and resources.
Key Factors Affecting Percent Yield
When calculating percent yield, several factors can significantly impact the result. Identifying these factors is the first step toward achieving high efficiency in chemical processes. Let’s explore some key factors that can lead to variations in yield.
Purity of Reactants
The purity of the reactants used in a chemical reaction directly influences both theoretical yield and actual yield. If impurities are present, they can either participate in the reaction or adversely affect the efficiency of the process. Chemists should always strive to use high-purity materials to achieve the best results. For instance, using a 90% pure reactant might lower the expected theoretical yield, as the effective concentration of the active material is reduced.
Reaction Conditions
Environmental factors such as temperature, pressure, and pH levels play a vital role in chemical reaction efficiency. In many reactions, maintaining optimal conditions is necessary to maximize product formation and minimize side reactions resulting in yield loss. For example, in exothermic reactions, controlling the temperature can help prevent by-products that can negatively impact percent yield. Consistency in replicating conditions across experiments is essential for accurate yield measurement.
Strategies for Improving Percent Yield
Improving yield percentage takes precision and careful planning. There are several strategies laboratories and production facilities can adopt to maximize their yields.
Optimize Reaction Conditions
One of the best ways to enhance percent yield is through optimization of reaction conditions. By adjusting parameters such as temperature and pressure, or by changing the time allowed for the reaction, chemists can often discover combinations that yield better results. Conducting preliminary experiments to identify the most favorable conditions is advisable in cases where yield improvement is essential.
Minimize Product Loss
Minimizing product loss during transferring, purifying, or storing materials is vital for improving yield analysis. Applying techniques such as careful filtration methods, minimizing transfer distances, and using inert atmospheres can substantially reduce the loss of products and improve actual yield. For example, using sealed containers might help prevent evaporation losses in volatile reactions.)
Practical Applications of Percent Yield
The application of percent yield calculation extends across various industries. From pharmaceuticals to industrial chemistry, percent yield serves as a benchmark for performance evaluation. Understanding how to calculate and interpret percent yield factors allows organizations to enhance their chemical production processes.
Case Study: Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, stringent quality and efficiency standards necessitate maximizing percent yield. Pharmaceutical companies meticulously analyze each step of their synthesis pathways to identify any losses and enhance their output. For instance, in synthesizing a new drug, scientists may repeatedly test different catalyst concentrations to identify a combination that produces the highest yield, reflected as a high percent yield in their experiments.
Real-time Yield Monitoring
Advanced technologies such as machine learning and data analytics provide new means for real-time yield monitoring. This dynamic growth in yield measurement frameworks allows for continuous adjustments to ensure optimal efficiency. By collecting data during the manufacturing process, companies can respond to issues affecting percent yield instantly, leading to improved performance.
Key Takeaways
- Percent yield is fundamental in evaluating chemical reaction efficiency.
- Factors such as reactant purity and reaction conditions heavily influence percent yield.
- Improving yield can be achieved through optimizing conditions and minimizing losses during product recovery.
- Applications in industries, particularly pharmaceuticals, highlight real-time monitoring for maximizing percent yield in reactions.
FAQ
1. What is the difference between actual yield and theoretical yield?
The actual yield is what you obtain from a reaction, while the theoretical yield is the maximum expected yield based on stoichiometric calculations. The percent yield derived from these two values informs about the efficiency of the reaction.
2. How can I improve my experiment’s percent yield?
To improve your percent yield, ensure you’re using high-purity reagents, optimize reaction conditions (temperature, pressure), and minimize product losses during transfer and analysis. Regularly evaluating these factors can lead to significant improvements.
3. Why is percent yield important in chemical economics?
In chemical economics, percent yield is important because it reflects the efficiency of resource use in production processes. Higher yields minimize waste, reduce costs, and improve profitability.
4. What are the common challenges that lead to low percent yield?
Common challenges include incomplete reactions, side reactions, and difficulties in product isolation. Environmental factors like temperature and humidity can also impact the yield outcomes.
5. How do industry standards affect percent yield?
Industry standards often dictate the acceptable range of percent yield for production processes. Meeting these standards is crucial for regulatory compliance and market competitiveness, making yield enhancement a priority for many organizations.
“`