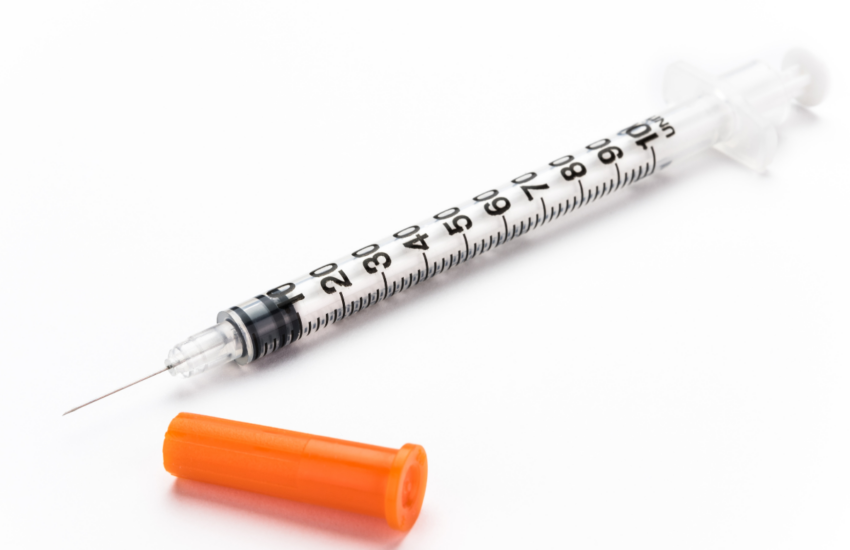
Understanding the Insulin Syringe: ml to Units Conversion
Insulin Syringe Measurements and Conversions
When managing diabetes effectively, knowing how to properly use an insulin syringe can make a significant difference in achieving desired blood sugar levels. Insulin syringes are designed with specific markings that help in accurately measuring insulin dosages. The standard concentration for injectable insulin, particularly in U-100 syringes, means that 1 ml equals 100 units of insulin. Understanding how to convert milliliters (ml) to units is critical for correct insulin administration and ensuring proper *insulin dosing*.
How Insulin Syringes are Marked
Insulin syringes typically have markings that correspond to the concentration of insulin in units. For instance, a U-100 insulin syringe clearly indicates that 1 ml contains 100 units. While different insulin concentrations may exist, U-100 is the most commonly used. In scenarios where a healthcare professional prescribes a different concentration, such as U-40 or U-500, it is crucial to consult the specific charts or guidelines for *insulin measurement* to avoid dosage errors and ensure *accurate insulin dosing*.
Importance of Accurate Insulin Measurement
Accurate measurement of insulin is vital for effective *diabetes management*. Even a slight miscalculation can lead to significant health consequences. When preparing an insulin injection, it’s essential to check the syringe for proper markings and to ensure that you’re drawing the correct amount of insulin. This practice not only aids in achieving optimal blood glucose levels, but also reduces the risks associated with both underdosing and overdosing. For example, gaining a deeper understanding of *insulin injection techniques* can provide the necessary confidence in managing one’s insulin therapy.
Practical Guide to Converting ml to Units in Insulin Syringes
Converting ml to units in insulin syringes requires a straightforward approach based on the concentration indicated on the syringe. Below, we outline a practical guide to make this conversion easily understandable for users managing their insulin injections.
Step-by-Step Conversion Process
Start by identifying the concentration of your insulin. If it reads U-100, you already know that 1 ml equals 100 units. For example, if you need to dose 0.5 ml, the calculation for conversion would be straightforward:
- 0.5 ml x 100 units/ml = 50 units of insulin.
It’s this simple math that allows *healthcare professionals* and patients alike to confidently check their *insulin dosage* and administer their medication effectively. Always remember to double-check your calculations and readjust if you are working with a syringe labeled with a different insulin concentration.
Common Insulin Syringe Sizes
Insulin syringes come in various sizes to accommodate different needs and dosing volumes. Common sizes include 0.3 ml, 0.5 ml, and 1 ml syringes, especially suitable for granular *diabetes care tools*. If patients require smaller doses or closer control, a 0.3 ml syringe is beneficial for more precise measurements. Alternatively, when larger doses are prescribed, a 1 ml syringe may be more suitable. Familiarizing yourself with different *syringe sizes for insulin* can improve the overall management of daily insulin needs.
Best Practices for Insulin Administration
To promote *proper insulin administration*, patients are encouraged to adhere to specific best practices. These practices not only ensure safety and efficacy but also enhance the management of diabetes on a day-to-day basis.
Safety Guidelines for Injection Techniques
Maintaining clean injection sites and following safety guidelines can substantially reduce the chance of infections or injuries. Proper washing of hands before handling syringes and selecting appropriate injection sites can lessen the risk associated with injecting insulin. Moreover, being aware of rotating injection sites is important to prevent tissue damage, which could impact insulin absorption and efficacy. Whether it’s for type 1 or type 2 diabetes, following clear and effective *insulin injection techniques* is key for long-term success.
Understanding Insulin Syringe Calibration
Calibration refers to the accuracy of the units marked on the syringe compared to the actual volume being administered. Over time, syringes, particularly with more frequent use, may experience calibration shift, where the markings no longer match precise volumes. Ensuring that syringes are periodically checked or replaced can keep this practice reliable. It stands as a reminder to consider both *syringe calibration* and efficacy in managing *blood sugar levels* effectively.
Concluding Thoughts on Insulin Dosage and Management
In summary, proper understanding of insulin syringes, along with the ability to convert ml to units accurately, is crucial for effective diabetes management. This knowledge empowers patients and caregivers alike. Staying informed about the types of syringes available, achieving mastering injection techniques, and adhering to safe practices all play a role in mastering *insulin delivery systems*.
Key Takeaways
- 1 ml of U-100 insulin equals 100 units.
- Understand the syringe concentrations to ensure accurate insulin measurement.
- Employ proper injection techniques and site rotation for safety.
- Regularly verify the calibration and condition of syringes used.
FAQ
1. How do I know what concentration my insulin is?
The concentration of the insulin will typically be specified on the vial or pen labeling. Common concentrations like U-100 or U-40 indicate how many units of insulin are present in 1 ml. Always check the label for specific details to ensure accurate dosing.
2. What should I do if I accidentally overdose on insulin?
If an overdose is suspected, contact a healthcare provider immediately. Depending on the amount and timing, treatment for hypoglycemia may be necessary. Always keep glucose tablets or sugary drinks nearby for quick access in emergencies.
3. Are there different types of insulin syringes available?
Yes, several types of insulin syringes exist, including different sizes like 0.3 ml, 0.5 ml, and 1 ml syringes. Additionally, certain syringes come with thinner needles or alternative needle gauges to suit personal comfort and needs during insulin administration.
4. How can I improve my insulin injection technique?
Practicing the injection technique regularly can be beneficial. Watching educational videos, consulting healthcare professionals, and participating in diabetes education programs can provide proper guidelines to enhance skills in insulin administration.
5. What are the risks of using expired insulin syringes?
Using expired insulin syringes can lead to ineffective dosing because the properties and calibration of the syringes might change over time, potentially leading to inaccurate insulin delivery. Always check expiration dates and dispose of syringes that are no longer valid.